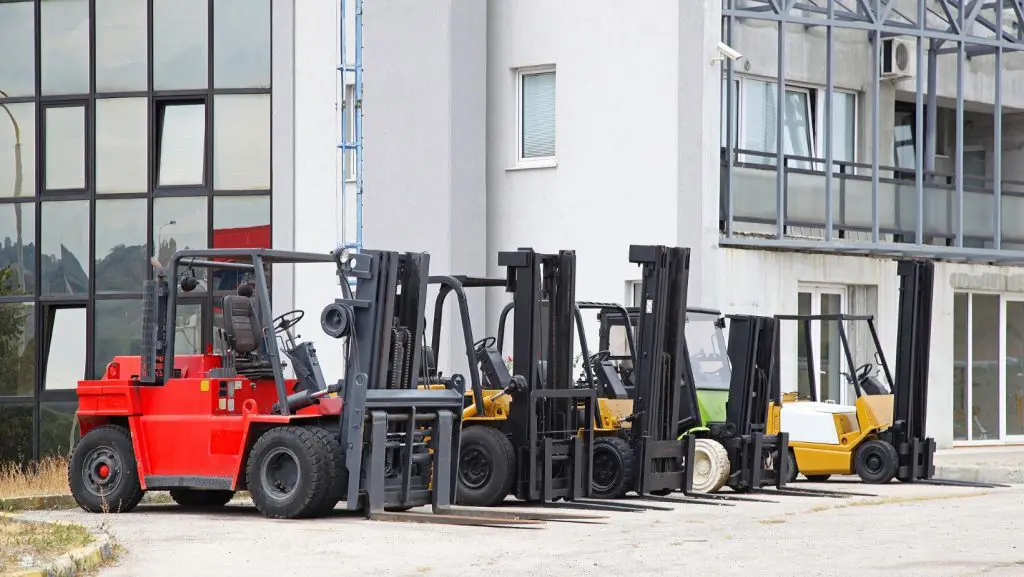
Forklifts are indispensable equipment in working environments, revolutionising how heavy goods are lifted, transported, and organised. Once you investigate forklift types, you will come across various power options. Forklifts can be powered in several ways, notably diesel, gas, or electric.
Choosing the right forklift depends on its tasks, frequency of performance, working conditions, and efficiency requirements. Our comprehensive guide will walk you through the types of forklifts and weigh the pros and cons of each fuel type, enabling you to make an informed decision about your investment.
- Types of Forklifts
- Diesel Forklifts
- Gas Forklifts
- Electric Forklifts
- How to Choose the Right Forklift
- Forklift Types FAQs
Types of Forklifts
Aside from the different types of forklift truck specifications, lifting capacities, and applications, another factor to consider is the fuel type. The three most commonly used forklifts are diesel, gas, or electric.
Due to their mechanical makeup, each forklift type is suited to different environmental conditions. Although they perform similar roles and can be very useful in their intended environments, understanding the differences between the three types can help businesses choose the most suitable option for their material handling needs.
Diesel Forklifts
Diesel forklifts are robust and powerful material-handling machines designed for heavy-duty applications. They run on diesel fuel and provide unrivalled lifting capacities, making them suitable for handling large loads in outdoor environments such as construction sites or shipping ports. Diesel forklifts offer reliable performance and durability, making them popular for industries with frequent and demanding tasks.
Pros
- Diesel forklifts are sturdily built, meaning the maintenance and repair costs will be reduced.
- They are ideal for outdoor use, where their fumes can easily escape without concentrating in an enclosed space, causing environmental or safety issues.
- Diesel forklifts have a higher torque than other forklifts, improving their performance on gradient surfaces and making them more powerful for towing duties.
- They are more fuel-efficient and do not require charging.
Cons
- Diesel-powered forklifts are not suitable for indoor use. It has been illegal to use a diesel forklift indoors since 2003.
- They release emissions that can be harmful to the environment. They can occasionally be used indoors with the addition of exhaust catalytic converters and purifiers, but these come with an added expense.
- Diesel engines are louder than other forklift fuel engines
- Due to their size, diesel forklifts may be inconvenient for some companies as they are bulkier and require more space for movement and storage.
Gas Forklifts
Gas forklifts, or LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) forklift trucks, are versatile material handling machines powered by propane or natural gas. They are popular in warehouses, distribution centres, manufacturing plants, and outdoor construction sites. They offer high performance and efficiency, making them suitable for indoor and outdoor applications. Gas forklifts are convenient for businesses requiring flexible and cost-effective material handling solutions.
Pros
- Gas-powered forklifts are widely available for purchase and hire, and they are initially cheaper than electric and diesel forklifts.
- These forklifts are built to be more compact than diesel forklifts, meaning they tend to be easier to manoeuvre, making them more versatile for indoor and outdoor use.
- Refuelling gas forklifts is quick and efficient. Propane tanks are easily replaceable, minimising downtime, unlike electric forklifts, which must be charged frequently.
- Gas forklifts emit lower emissions than diesel forklifts, making them more environmentally friendly.
Cons
- Gas forklifts require a steady supply of propane or natural gas, which is only readily available from companies in specific areas.
- Although gas forklifts are quieter than diesel forklifts, they are noisier than electric forklifts, which may be a consideration for indoor applications where quiet operation is required.
- They require regular maintenance to ensure that they are performing optimally and complying with safety regulations
- Although gas forklifts emit fewer emissions, they still produce carbon monoxide fumes, posing health and safety risks to workers in poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
Electric Forklifts
Electric forklift trucks are the most energy-efficient option for forklift operators. Unlike gas or diesel trucks, electric forklifts produce zero emissions, making them ideal for indoor use in warehouses, distribution centres, and manufacturing facilities. They offer quiet operation, low maintenance requirements, and cost-effective long-term operation. However, they are not suitable for all environments.
Pros
- Electric forklifts operate quietly, reducing noise pollution in indoor environments and providing a more comfortable workspace for operators.
- These forklifts are much more cost-effective as recharging the battery overnight is much lower than refilling a diesel tank or replacing a gas bottle.
- Electric forklifts offer precise control and seamless operation, making them suitable for tasks requiring precise handling and manoeuvrability.
- They have fewer maintenance requirements as they are built to have fewer moving parts. This reduces operational costs.
Cons
- The initial costs of purchasing an electric forklift are higher than those of other options. This is primarily due to the added overhead costs of buying the battery and installing a charger in your workspace.
- Electric forklifts must be charged overnight, which increases downtime. This can be combated by purchasing extra batteries to enable round-the-clock operation, but it comes at an added expense.
- Due to the large number of electrical components, using them indoors in wet or damp conditions is not recommended.
- The higher point loadings on the wheels and axles of electric forklifts mean they require a smoother floor surface to operate safely as opposed to gas or diesel trucks.
How to Choose the Right Forklift
Choosing the right forklift depends on several factors, from operation requirements to budget.
Here are some considerations to help you make an informed decision:
- Environment: Determine whether your forklift will primarily be used indoors or outdoors and the conditions of the surfaces on which it will be driven. Assess any space constraints, such as narrow aisles, for which the level of manoeuvrability is essential.
- Emissions: If your forklift will be used primarily indoors or in enclosed spaces, it may be worth considering an electric forklift that will not impact air quality. Diesel or gas forklifts may be more appropriate for outdoor spaces.
- Operating Costs & Maintenance: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase cost, fuel or electricity costs, maintenance expenses and potential downtime. Electric forklifts are initially more expensive but require less maintenance, potentially making them more cost-effective.
- Performance Requirements: Determine the lifting capacity and performance capabilities you require. Gas and diesel forklifts offer higher lifting capacities and faster acceleration than electric forklifts, making them more suitable for outdoor use. In contrast, electric forklifts favour smooth and quiet operation, making them ideal for indoor applications for precise material handling.
Forklift Types FAQs
Can diesel forklifts be used indoors?
Regulations surround the use of diesel forklifts indoors. In most cases, diesel forklifts should only be used in outdoor spaces where the emissions can escape freely. They can be used indoors because the area is well-ventilated, and the operation follows safety guidelines. These guidelines state that if diesel forklifts are used indoors for prolonged periods of time, the building must have roof and wall extractors.
How much diesel does a forklift use per hour?
A diesel forklift will consume around 2.6 litres of diesel per hour.
How often should you charge an electric forklift?
Generally, your forklift should be recharged after an 8-hour shift or when it has discharged more than 30%. If you charge your forklift too frequently, its battery life can be shortened.
Learn More About Forklift Types with HL Training
At HL Training, our team of forklift experts have extensive knowledge spanning the different types of forklifts and how to choose the right truck for your requirements. With your forklift choice comes the requirement for accredited training.
We are dedicated to ensuring that all forklift operators receive high-quality training tailored to their forklift to maximise operational efficiency and safety. Whether you are a beginner needing an in-depth training course or an experienced forklift driver needing a refresh, we have a range of courses available. Contact us today to learn more about choosing the right forklift for you and receiving the appropriate training.